Countries caught in the poverty population trap have experienced a myriad of challenges that have hindered their economic and social development. This multifaceted issue stems from a complex interplay of economic, political, social, environmental, international, and historical factors, each contributing to a vicious cycle of poverty.
The low income levels that characterize these countries create a self-perpetuating cycle, as limited resources constrain investment in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, further exacerbating poverty. Political instability and weak governance often compound these challenges, making it difficult to implement effective policies and attract foreign investment.
Economic Factors
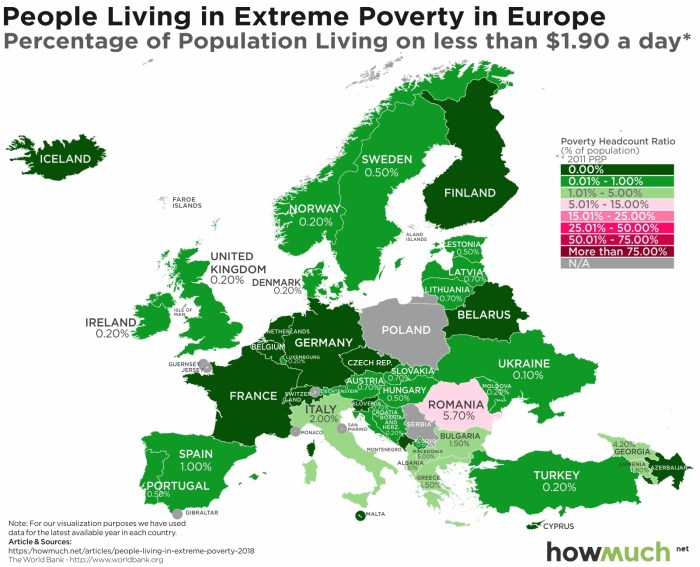
Low income levels are a major factor trapping countries in poverty. Countries with low incomes often lack the resources to invest in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, which are essential for economic development. This lack of investment leads to a cycle of poverty, as low incomes make it difficult to save and invest, which in turn makes it difficult to break out of poverty.
There are many examples of countries that have struggled to escape low income status. One example is Haiti, which has been plagued by poverty for centuries. Haiti’s low income levels are due to a number of factors, including political instability, corruption, and natural disasters.
Another example is Afghanistan, which has been in a state of war for decades. The war has destroyed much of Afghanistan’s infrastructure and economy, and has made it difficult for the country to attract foreign investment.
Foreign aid can play a role in helping countries to reduce poverty. However, foreign aid is often not enough to lift countries out of poverty. In order to truly escape poverty, countries need to implement sound economic policies that promote economic growth and create jobs.
Political Factors
Political instability can also contribute to poverty traps. Countries that are politically unstable often have weak governments that are unable to provide basic services to their citizens. This lack of services can lead to a cycle of poverty, as people are unable to access the resources they need to improve their lives.
There are many examples of countries that have experienced poverty traps due to political factors. One example is Somalia, which has been in a state of civil war for decades. The war has destroyed much of Somalia’s infrastructure and economy, and has made it difficult for the country to attract foreign investment.
Another example is the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has been plagued by political instability and violence for decades. The violence has displaced millions of people and has made it difficult for the government to provide basic services to its citizens.
Implementing effective poverty reduction policies in politically unstable environments is a challenge. However, there are a number of things that can be done. One important step is to build strong and inclusive governments that are able to provide basic services to their citizens.
Another important step is to promote peace and stability, which will create a more conducive environment for economic development.
Social Factors
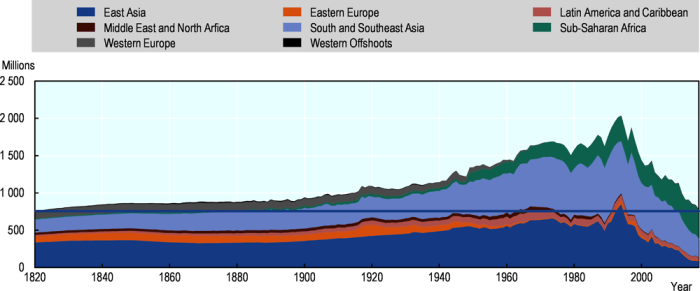
Inequality is another factor that can perpetuate poverty traps. In countries with high levels of inequality, the wealthy often have access to better education, healthcare, and other resources than the poor. This inequality can make it difficult for the poor to break out of poverty.
There are many examples of countries that have experienced poverty traps due to inequality. One example is Brazil, which has one of the highest levels of inequality in the world. The gap between the rich and the poor in Brazil is so large that it has created a cycle of poverty, as the poor are unable to access the resources they need to improve their lives.
Social stratification can also limit opportunities for economic advancement. In countries with rigid social hierarchies, it can be difficult for people from lower social classes to move up the economic ladder. This can lead to a cycle of poverty, as people are unable to break out of the social class into which they were born.
Cultural norms and beliefs can also play a role in poverty traps. In some cultures, there may be a belief that poverty is inevitable or that it is a punishment for past sins. This belief can make it difficult for people to break out of poverty, as they may not believe that they deserve a better life.
FAQ Resource: Countries Caught In The Poverty Population Trap Have Experienced
What are the key factors that contribute to poverty traps?
Economic, political, social, environmental, international, and historical factors all play a role in creating and perpetuating poverty traps.
How does political instability impact poverty traps?
Political instability can make it difficult to implement effective poverty reduction policies and attract foreign investment, further exacerbating poverty.
What is the role of social inequality in poverty traps?
Social inequality can limit opportunities for economic advancement and perpetuate poverty traps by concentrating wealth and resources in the hands of a few.